My mother has alzheimer's and dementia and was becoming agressive. We dive her 5mg of Urb in the morning and 5mg in the afternoon and she is calm and focused. It has been a godsend.
The Mile High Aerovape is, without question, the absolute best!! Hands down! Its been almost 2 months and still going strong. Whats even more impressive? Right after I got it, I accidentally ran it through a FULL washer cycle… and IT SURVIVE like a champ. TWO months later, it works perfectly!!! Durable, reliable, and seriously impressive!! Keep up the good work URB!!!!
I have tried many types of CBD products and I find URB to be the best on the market. Not only is it effective but it also the most economical. I'm a customer for life.
I use Dreamland Gummies as a sleep aid. They do the job and I will keep buying them!
Honestly, I’m not one to leave reviews, but URB is by far the best company in Hemp Derived products that I’ve ever purchased from. So much so, that I only look up URB now whenever I need to stock up. I love their cartridges—they have the best terpene-cannabinoid blends for every effect, it seems. My favorites are the indicas. Anything from just simple relaxation on a day off, to huge relief after a long, stressful day, they’ve got your remedy. Thanks Lifted Made!
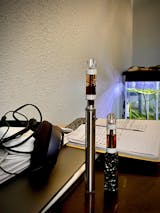
In the pic, I have a Flight Fuel 710 relax, followed by a little chaser of Vape Cay London for another layer of smooth relaxation… best way to unwind ;)